Abstract
In this research, a supercritical CO2-ethanol extraction was optimized to obtain a green coffee oil rich in bioactive compounds. A face-centered central composite design was used to evaluate the effect of temperature (50–70 °C), extraction pressure (15.0–30.0 MPa), and cosolvent content (5–20%) on the extraction yield and total phenolic compound content of green coffee supercritical extract (GCSE). The experimental data were fitted to a second-order polynomial model. According to the statistical analyses, the lack of fit was not significant for either mathematical model. From the response surface plots, the extraction pressure and cosolvent content significantly impacted the extraction yield, while the total phenolic compound content was impacted by temperature and cosolvent content. The optimal conditions were a 20% cosolvent content, a pressure of 30 MPa, and a temperature of 62 °C, which predicted an extraction yield of 7.7% with a total phenol content of 5.4 mg gallic acid equivalent g GCSE−1. The bioactive compounds included 5-caffeoylquinic acid (11.53–17.91 mg g GCSE−1), caffeine (44.76–79.51 mg g GCSE−1), linoleic acid (41.47–41.58%), and palmitic acid (36.07–36.18%). Our results showed that GCSE has the outstanding chemical quality and antioxidant potential, suggesting that GCSE can be used as a functional ingredient.

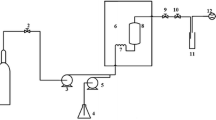
(Adapted from Waters (2018))

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GCSE:
-
Green coffee supercritical extract
- TEAC:
-
Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity
- TPC:
-
Total phenolic compound content
- EY:
-
Extraction yield
- Co :
-
Cosolvent content
- GCSEEY :
-
Green coffee supercritical extract at optimal yield extraction conditions
- GCSEOP :
-
Green coffee supercritical extract under optimal conditions
References
Ahangari B, Sargolzaei J (2013) Extraction of lipids from spent coffee grounds using organic solvents and supercritical carbon dioxide. J Food Process Preserv 37:1014–1021. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4549.2012.00757.x
Akay S, Alpak I, Yesil-Celiktas O (2011) Effects of process parameters on supercritical CO2 extraction of total phenols from strawberry (Arbutus unedo L.) fruits: an optimization study. J Sep Sci 34:1925–1931. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201100361
Andrade KS, Gonalvez RT, Maraschin M et al (2012) Supercritical fluid extraction from spent coffee grounds and coffee husks: antioxidant activity and effect of operational variables on extract composition. Talanta 88:544–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.11.031
Araújo MN, Azevedo AQPL, Hamerski F et al (2019) Enhanced extraction of spent coffee grounds oil using high-pressure CO2 plus ethanol solvents. Ind Crops Prod 141:111723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111723
Babova O, Occhipinti A, Maffei ME (2016) Chemical partitioning and antioxidant capacity of green coffee (Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora) of different geographical origin. Phytochemistry 123:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.01.016
Banchero M, Pellegrino G, Manna L (2013) Supercritical fluid extraction as a potential mitigation strategy for the reduction of acrylamide level in coffee. J Food Eng 115:292–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.10.045
Barbosa HMA, de Melo MMR, Coimbra MA et al (2014) Optimization of the supercritical fluid coextraction of oil and diterpenes from spent coffee grounds using experimental design and response surface methodology. J Supercrit Fluids 85:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2013.11.011
Bitencourt RG, Ferreira NJ, Oliveira AL et al (2018) High pressure phase equilibrium of the crude green coffee oil—CO2—ethanol system and the oil bioactive compounds. J Supercrit Fluids 133:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2017.09.017
Bitencourt RG, Mello FMPA, Cabral FA, Meirelles AJA (2020) High-pressure fractionation of spent coffee grounds oil using green solvents. J Supercrit Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2019.104689
Cavalcanti RN, Meireles MAA, Sp C (2012) Fundamentals of supercritical fluid extraction. Compr Sampl Sample Prep 2:117–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-381373-2.10039-0
Cornelio-Santiago HP, Gonçalves CB, de Oliveira NA, de Oliveira AL (2017) Supercritical CO2 extraction of oil from green coffee beans: Solubility, triacylglycerol composition, thermophysical properties and thermodynamic modelling. J Supercrit Fluids 128:386–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2017.05.030
Couto RM, Fernandes J, da Silva MDRG, Simões PC (2009) Supercritical fluid extraction of lipids from spent coffee grounds. J Supercrit Fluids 51:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2009.09.009
de Azevedo ABA, Mazzafera P, Mohamed RS (2008) Extraction of caffeine, chlorogenic acids and lipids from green coffee beans using supercritical carbon dioxide and cosolvents. Braz J Chem Eng 25:543–552. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322008000300012
De Oliveira PMA, De Almeida RH, De Oliveira NA et al (2014) Enrichment of diterpenes in green coffee oil using supercritical fluid extraction—characterization and comparison with green coffee oil from pressing. J Supercrit Fluids 95:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2014.08.016
Efthymiopoulos I, Hellier P, Ladommatos N et al (2019) Effect of solvent extraction parameters on the recovery of oil from spent coffee grounds for biofuel production. Waste Biomass Valoriz 10:253–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0061-4
Farah A (2012) Coffee constituents. In: Chu Y-F (ed) Coffee: emerging health effects and disease prevention, 1st edn. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Hoboken, pp 21–58
Farah A, Donangelo CM (2006) Phenolic compounds in coffee. Braz J Plant Physiol 18:23–36. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-04202006000100003
Frost-Meyer NJ, Logomarsino JV (2012) Impact of coffee components on inflammatory markers: a review. J Funct Foods 4:819–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2012.05.010
Granados-Vallejo M, Espinosa-Andrews H, Guatemala-Morales MG et al (2019) Oxidative stability of green coffee oil (Coffea arabica) microencapsulated by spray drying. Processes 7:734
Hurtado-Benavides A, Dorado DA, Sánchez-Camargo ADP (2016) Study of the fatty acid profile and the aroma composition of oil obtained from roasted Colombian coffee beans by supercritical fluid extraction. J Supercrit Fluids 113:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2016.03.008
Ilgaz S, Sat IG, Polat A (2018) Effects of processing parameters on the caffeine extraction yield during decaffeination of black tea using pilot-scale supercritical carbon dioxide extraction technique. J Food Sci Technol 55:1407–1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3055-8
Jeszka-Skowron M, Stanisz E, De Peña MP (2016) Relationship between antioxidant capacity, chlorogenic acids and elemental composition of green coffee. LWT Food Sci Technol 73:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.06.018
Jitrangsri K, Chaidedgumjorn A, Satiraphan M (2020) Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) optimization of trans-resveratrol from peanut kernels (Arachis hypogaea) by experimental design. J Food Sci Technol 57:1486–1494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04184-9
Kopcak U, Mohamed RS (2005) Caffeine solubility in supercritical carbon dioxide/co-solvent mixtures. J Supercrit Fluids 34:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2004.11.016
Liang N, Kitts DD (2015) Role of chlorogenic acids in controlling oxidative and inflammatory stress conditions. Nutrients 8:16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8010016
Ludwig IA, Clifford MN, Lean MEJ et al (2014) Coffee: biochemistry and potential impact on health. Food Funct 5:1695–1717. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00042K
Machmudah S, Kitada K, Sasaki M et al (2011) Simultaneous extraction and separation process for coffee beans with supercritical CO2 and water. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:2227–2235. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101252w
Marques LLM, Panizzon GP, Aguiar BAA et al (2016) Guaraná (Paullinia cupana) seeds: selective supercritical extraction of phenolic compounds. Food Chem 212:703–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.06.028
Martínez-López S, Sarriá B, Mateos R, Bravo-Clemente L (2019) Moderate consumption of a soluble green/roasted coffee rich in caffeoylquinic acids reduces cardiovascular risk markers: results from a randomized, cross-over, controlled trial in healthy and hypercholesterolemic subjects. Eur J Nutr 58:865–878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1726-x
Ochoa Becerra MA (2020) Extracción de cafeína y ácido clorogénico de la pulpa de café por medio de tecnologías no convencionales y su purificación mediante resinas poliméricas. Centro de Investigación y Asistencia en Tecnología y Diseño del Estado de Jalisco
Onakpoya I, Terry R, Ernst E (2011) The use of green coffee extract as a weight loss supplement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Gastroenterol Res Pract. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/382852
Palmioli A, Ciaramelli C, Tisi R et al (2017) Natural compounds in cancer prevention: effects of coffee extracts and their main polyphenolic component, 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid, on oncogenic Ras proteins. Chem Asian J 12:2457–2466. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201700844
Research-Reports 360 (2020) Global Chlorogenic Acid Market Research Report 2020. https://www.360researchreports.com/global-chlorogenic-acid-market-15083142. Accessed 28 Apr 2020
Ruiz-Palomino P, Guatemala-Morales G, Mondragón-Cortéz PM et al (2019) Empirical model of the chlorogenic acid degradation kinetics during coffee roasting in a spouted bed. Rev Mex Ing Quim 18:387–396. https://doi.org/10.24275/uam/izt/dcbi/revmexingquim/2019v18n2/Ruiz
Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera (2019) Panorama Agroalimentario 2019. Ciudad de México
Waters (2018) Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE) Systems. In: Waters Prep SFE Syst. http://www.waters.com/waters/en_US/SFE-extraction-equipment/nav.htm?locale=en_US&cid=134614431. Accessed 28 Apr 2020
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the CONACYT [CB-2015-01-258118 and FORDECYT 292474]. The authors would like to thank CONACYT for scholarship No. #413405 (Barajas Álvarez, P.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barajas-Álvarez, P., Castillo-Herrera, G.A., Guatemala-Morales, G.M. et al. Supercritical CO2-ethanol extraction of oil from green coffee beans: optimization conditions and bioactive compound identification. J Food Sci Technol 58, 4514–4523 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04933-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04933-1