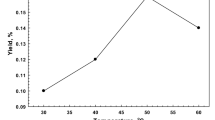
Abstract
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are evolving as green extraction media in the search for efficient extraction of bioactive compounds. In the current study, four different choline chloride based DESs (eutectics of Choline chloride with ethylene glycol, malic acid, oxalic acid, and tartaric acid) were prepared with their physico-chemical properties and cytotoxicity evaluation. The FT-IR spectra of all solvents showed a very strong and broad band at 3350–3450 cm−1 due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding between choline chloride and hydrogen bond donors. The DESs were employed for the ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) of bioactive compounds from Cymbopogon citratus (lemongrass) to signify the extraction efficiency of DESs over aqueous methanol. The optimization of extraction parameters (time, temperature and biomass to solvent ratio) was done using Box–Behnken design (BBD). These solvents have negligible values of cytotoxicity in the range of 3.67 to 10.20%. The extraction yields obtained with DESs were significantly higher than aqueous methanol. The highest quantities of total phenolic contents (TPC) 116 mg GAE/g dry matter, total flavonoids contents (TFC) 98 mg QE/g dry matter and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical inhibition 95% were assessed with choline chloride/ethylene glycol solvent due to reduced viscosity. The maximum inhibition zones 45 ± 1.2 mm and 40 ± 1.3 mm against bacterial strains S. aureus and E. coli, respectively and 38 ± 1.2 mm and 29 ± 0.5 mm against fungal strains F. solani and A. niger, respectively were observed by choline chloride/ethylene glycol solvent. The DESs have revealed considerable high extraction yield due to extensive hydrogen bonding, which ultimately relates to the higher antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. The developed DESs would be the best alternative for the green and efficient extraction of phenolic compounds from natural sources.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.B. Barbieri, C. Goltz, F.B. Cavalheiro, A.T. Toci, L. Igarashi-Mafra, M.R. Mafra, Deep eutectic solvents applied in the extraction and stabilization of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) phenolic compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 144, 112049 (2020)
P. Zhou, X. Wang, P. Liu, J. Huang, C. Wang, M. Pan, Z. Kuang, Enhanced phenolic compounds extraction from Morus alba L. leaves by deep eutectic solvents combined with ultrasonic-assisted extraction. Ind. Crops Prod. 120, 147–154 (2018)
Y. Zhao, P. Wang, W. Zheng, G. Yu, Z. Li, Y. She, M. Lee, Three-stage microwave extraction of cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) Seed essential oil with natural deep eutectic solvents. Ind. Crops Prod. 140, 111660 (2019)
M.E. Alañón, M. Ivanović, A.M. Gómez-Caravaca, D. Arráez-Román, A. Segura-Carretero, Choline chloride derivative-based deep eutectic liquids as novel green alternative solvents for extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaf. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 1685–1701 (2020)
D. Krishnaiah, R. Sarbatly, R. Nithyanandam, A review of the antioxidant potential of medicinal plant species. Food Bioprod. Process. 89, 217–233 (2011)
G. Costa, J.P. Ferreira, C. Vitorino, M.E. Pina, J.J. Sousa, I.V. Figueiredo, M.T. Batista, Polyphenols from Cymbopogon citratus leaves as topical anti-inflammatory agents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 178, 222–228 (2016)
S. Bedin, F.M. Netto, N. Bragagnolo, O.P. Taranto, Reduction of the process time in the achieve of rice bran protein through ultrasound-assisted extraction and microwave-assisted extraction. Sep. Sci. Technol. 55, 300–312 (2020)
Z. Naseem, M. Zahid, M.A. Hanif, M. Shahid, Environmentally friendly extraction of bioactive compounds from Mentha arvensis using deep eutectic solvent as green extraction media. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 29, 3749–3757 (2020)
B. Wang, Y. Hui, L. Liu, A. Zhao, Y.-S. Chiou, F. Zhang, M.-H. Pan, Optimized extraction of phenolics from jujube peel and their anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 67, 1666–1673 (2019)
B. Yang, M. Zhang, H. Weng, Y. Xu, L. Zeng, Optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) of kinsenoside compound from Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) lindl by response surface methodology (RSM). Molecules 25, 193 (2020)
K. Radošević, N. Ćurko, V.G. Srček, M.C. Bubalo, M. Tomašević, K.K. Ganić, I.R. Redovniković, Natural deep eutectic solvents as beneficial extractants for enhancement of plant extracts bioactivity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 73, 45–51 (2016)
A. García, E. Rodríguez-Juan, G. Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, J.J. Rios, J. Fernández-Bolaños, Extraction of phenolic compounds from virgin olive oil by deep eutectic solvents (DESs). Food Chem. 197, 554–561 (2016)
M. Riaz, N. Rasool, I. Bukhari, M. Shahid, M. Zubair, K. Rizwan, U. Rashid, In vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxicity and GC-MS analysis of Mazus goodenifolius. Molecules 17, 14275–14287 (2012)
Y. Huang, F. Feng, J. Jiang, Y. Qiao, T. Wu, J. Voglmeir, Z.-G. Chen, Green and efficient extraction of rutin from tartary buckwheat hull by using natural deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 221, 1400–1405 (2017)
K. Hao, W. Hu, M. Hou, D. Cao, Y. Wang, Q. Guan, X. Zhang, A. Wang, J. Yu, B. Guo, Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of total phenolics from Citrus aurantium L. blossoms and evaluation of free radical scavenging, anti-HMG-CoA reductase activities. Molecules 24, 2368 (2019)
S.A. Heleno, P. Diz, M. Prieto, L. Barros, A. Rodrigues, M.F. Barreiro, I.C. Ferreira, Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction to obtain mycosterols from Agaricus bisporus L. by response surface methodology and comparison with conventional Soxhlet extraction. Food Chem. 197, 1054–1063 (2016)
F. Giusti, G. Caprioli, M. Ricciutelli, S. Vittori, G. Sagratini, Determination of fourteen polyphenols in pulses by high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) and correlation study with antioxidant activity and colour. Food Chem. 221, 689–697 (2017)
Q.D. Do, A.E. Angkawijaya, P.L. Tran-Nguyen, L.H. Huynh, F.E. Soetaredjo, S. Ismadji, Y.-H. Ju, Effect of extraction solvent on total phenol content, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of Limnophila aromatica. J. Food Drug Anal. 22, 296–302 (2014)
Z. Xu, S. Feng, S. Shen, H. Wang, M. Yuan, J. Liu, Y. Huang, C. Ding, The antioxidant activities effect of neutral and acidic polysaccharides from Epimedium acuminatum Franch. on Caenorhabditis elegans. Carbohydr. Polym. 144, 122–130 (2016)
A. Venditti, C. Frezza, F. Sciubba, M. Serafini, A. Bianco, K. Cianfaglione, G. Lupidi, L. Quassinti, M. Bramucci, F. Maggi, Volatile components, polar constituents and biological activity of tansy daisy (Tanacetum macrophyllum (Waldst. et Kit.) Schultz Bip.). Ind. Crops Prod. 118, 225–235 (2018)
N. Mehmood, M. Zubaır, K. Rızwan, N. Rasool, M. Shahid, V.U. Ahmad, Antioxidant, antimicrobial and phytochemical analysis of cichoriumintybus seeds extract and various organic fractions. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 11, 1145 (2012)
S.L. Perkins, P. Painter, C.M. Colina, Experimental and computational studies of choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 59, 3652–3662 (2014)
C. Florindo, F. Lima, B.D. Ribeiro, I.M. Marrucho, Deep eutectic solvents: overcoming 21st century challenges. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 18, 31–36 (2019)
A. Airinei, D.L. Isac, M. Homocianu, C. Cojocaru, C. Hulubei, Solvatochromic analysis and DFT computational study of an azomaleimide derivative. J. Mol. Liq. 240, 476–485 (2017)
O.A. Vydrov, T. Van Voorhis, Nonlocal van der Waals density functional made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 063004 (2009)
A. Benarfa, N. Gourine, S. Hachani, M. Harrat, M. Yousfi, Optimization of ultrasound‐assisted extraction of antioxidative phenolic compounds from Deverra scoparia Coss. & Durieu (flowers) using response surface methodology. J. Food Process. Preserv. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14514
M. Kazemi, R. Karim, H. Mirhosseini, A.A. Hamid, Optimization of pulsed ultrasound-assisted technique for extraction of phenolics from pomegranate peel of Malas variety: Punicalagin and hydroxybenzoic acids. Food Chem. 206, 156–166 (2016)
G. Ramadoss, K. Muthukumar, Ultrasound assisted metal chloride treatment of sugarcane bagasse for bioethanol production. Renew. Energy 99, 1092–1102 (2016)
M. Ramić, S. Vidović, Z. Zeković, J. Vladić, A. Cvejin, B. Pavlić, Modeling and optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenolic compounds from Aronia melanocarpa by-products from filter-tea factory. Ultrason. Sonochem. 23, 360–368 (2015)
A. Yadav, S. Pandey, Densities and viscosities of (choline chloride + urea) deep eutectic solvent and its aqueous mixtures in the temperature range 293.15 K to 363.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 59, 2221–2229 (2014)
C. Corbin, T. Fidel, E.A. Leclerc, E. Barakzoy, N. Sagot, A. Falguiéres, S. Renouard, J.-P. Blondeau, C. Ferroud, J. Doussot, Development and validation of an efficient ultrasound assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) seeds. Ultrason. Sonochem. 26, 176–185 (2015)
W. Bi, M. Tian, K.H. Row, Evaluation of alcohol-based deep eutectic solvent in extraction and determination of flavonoids with response surface methodology optimization. J. Chromatogr. A 1285, 22–30 (2013)
L.G. d’Alessandro, K. Kriaa, I. Nikov, K. Dimitrov, Ultrasound assisted extraction of polyphenols from black chokeberry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 93, 42–47 (2012)
K.N. Prasad, E. Yang, C. Yi, M. Zhao, Y. Jiang, Effects of high pressure extraction on the extraction yield, total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of longan fruit pericarp. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 10, 155–159 (2009)
W. Wang, J. Jung, E. Tomasino, Y. Zhao, Optimization of solvent and ultrasound-assisted extraction for different anthocyanin rich fruit and their effects on anthocyanin compositions. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 72, 229–238 (2016)
Y. Dai, J. van Spronsen, G.-J. Witkamp, R. Verpoorte, Y.H. Choi, Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 766, 61–68 (2013)
Y. Dai, R. Verpoorte, Y.H. Choi, Natural deep eutectic solvents providing enhanced stability of natural colorants from safflower (Carthamus tinctorius). Food Chem. 159, 116–121 (2014)
M.K. AlOmar, M. Hayyan, M.A. Alsaadi, S. Akib, A. Hayyan, M.A. Hashim, Glycerol-based deep eutectic solvents: physical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 215, 98–103 (2016)
O.A. Aiyegoro, A.I. Okoh, Preliminary phytochemical screening and in vitro antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract of Helichrysum longifolium DC. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 10, 21 (2010)
M.C. Bubalo, N. Ćurko, M. Tomašević, K.K. Ganić, I.R. Redovniković, Green extraction of grape skin phenolics by using deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 200, 159–166 (2016)
P. Katsampa, E. Valsamedou, S. Grigorakis, D.P. Makris, A green ultrasound-assisted extraction process for the recovery of antioxidant polyphenols and pigments from onion solid wastes using Box-Behnken experimental design and kinetics. Ind. Crops Prod. 77, 535–543 (2015)
Z. Naseem, M. Zahid, M.A. Hanif, M. Shahid, Green extraction of ethnomedicinal compounds from Cymbopogon citratus Stapf using hydrogen-bonded supramolecular network. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1, 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2020.1781894
Acknowledgements
This study was accomplished with partial financial support of HEC through Access to Scientific Instrumentation Program (ASIP) under Grant No. 20-2(8)/ASIP/R&D/HEC/17/00038(HEJ). The computational structure were performed on resources provided by the Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing (SNIC) at Umeå University, 901 87, Umeå, Sweden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naseem, Z., Iqbal, J., Zahid, M. et al. Use of hydrogen-bonded supramolecular eutectic solvents for eco-friendly extraction of bioactive molecules from Cymbopogon citratus using Box–Behnken design. Food Measure 15, 1487–1498 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00744-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00744-2