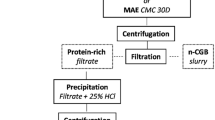
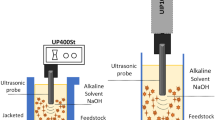
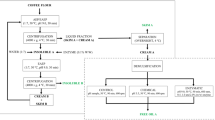
Abstract
Coffee silverskin (CSS) is a coffee by-product obtained during the coffee roasting process and a potential source of proteins (14–19% protein content). In this study, conventional extraction (CE) and novel extraction methods were investigated for protein extraction from CSS. Optimum extraction pH and concentration for conventional acid and alkali extraction were studied. In addition, ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), which have been widely recognised as efficient and economic novel extraction techniques, were employed to enhance the protein extraction from CSS using alkaline and acid extraction. Among the extraction techniques studied, MAE was found to generate the highest yield of protein recovery, 43.53% of recovery with an average molecular weight of 6.64 kDa. Comparing with the conventional sequential extraction using NaOH followed by HCl at two different concentrations (0.2 M and 0.6 M), the recovery yields were significantly increased by 2.8-fold and 2.3-fold by applying UAE, and by 5.8-fold and 7-fold by applying MAE. The present work shows that UAE and MAE have potential to be rapid and effective tools for protein extraction from coffee silverskin. In this study, extracted proteins and raw material were characterised considering the molecular weight and the amino acid profile as well as its nutritional composition and its mineral contents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso E (2018) The role of supercritical fluids in the fractionation pretreatments of a wheat bran-based biorefinery. J Supercrit Fluids 133:603–614
Álvarez C, Lélu P, Lynch SA, Tiwari BK (2018) Optimised protein recovery from mackerel whole fish by using sequential acid/alkaline isoelectric solubilization precipitation (ISP) extraction assisted by ultrasound. LWT 88:210–216
Ballesteros LF, Teixeira JA, Mussatto SI (2014) Chemical, functional, and structural properties of spent coffee grounds and coffee silverskin. Food Bioprocess Technol 7:3493–3503
Barbosa MDSG, Scholz MBDS, Kitzberger CSG, Benassi MDT (2019) Correlation between the composition of green Arabica coffee beans and the sensory quality of coffee brews. Food Chem 292:275–280
Capellini MC, Giacomini V, Cuevas MS, Rodrigues CEC (2017) Rice bran oil extraction using alcoholic solvents: physicochemical characterization of oil and protein fraction functionality. Ind Crop Prod 104:133–143
Celiktas MS, Kirsch C, Smirnova I (2014) Cascade processing of wheat bran through a biorefinery approach. Energy Convers Manag 84:633–639
Celus I, Brijs K, Delcour JA (2009) Fractionation and characterization of brewers’ spent grain protein hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem 57:5563–5570
Contreras MDM, Lama-Muñoz A, Manuel Gutiérrez-Pérez J, Espínola F, Moya M, Castro E (2019) Protein extraction from agri-food residues for integration in biorefinery: potential techniques and current status. Bioresour Technol 280:459–477
Ekezie F-GC, Sun D-W, Cheng J-H (2017) Acceleration of microwave-assisted extraction processes of food components by integrating technologies and applying emerging solvents: a review of latest developments. Trends in Food Science and Technology 67:160–172
Ekezie F-GC, Sun D-W, Han Z, Cheng J-H (2017) Microwave-assisted food processing technologies for enhancing product quality and process efficiency: a review of recent developments. Trends in Food Science and Technology 67:58–69
Görgüç A, Bircan C, Yilmaz FM (2019) Sesame bran as an unexploited by-product: effect of enzyme and ultrasound-assisted extraction on the recovery of protein and antioxidant compounds. Food Chem 283:637–645
Guo Q, Sun D-W, Cheng J-H, Han Z (2017) Microwave processing techniques and their recent applications in the food industry. Trends in Food Science and Technology 67:236–247
Han S-W, Chee K-M, Cho S-J (2015) Nutritional quality of rice bran protein in comparison to animal and vegetable protein. Food Chem 172:766–769
Hou F, Ding W, Qu W, Oladejo AO, Xiong F, Zhang W, He R, Ma H (2017) Alkali solution extraction of rice residue protein isolates: influence of alkali concentration on protein functional, structural properties and lysinoalanine formation. Food Chem 218:207–215
Iriondo-Dehond A, Aparicio García N, Fernandez-Gomez B, Guisantes-Batan E, Velázquez Escobar F, Blanch GP, San Andres MI, Sanchez-Fortun S, Del Castillo MD (2019) Validation of coffee by-products as novel food ingredients. Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 51:194–204
Jambrak AR, Mason TJ, Lelas V, Paniwnyk L, Herceg Z (2014) Effect of ultrasound treatment on particle size and molecular weight of whey proteins. J Food Eng 121:15–23
Janissen B, Huynh T (2018) Chemical composition and value-adding applications of coffee industry by-products: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 128:110–117
Jia J, Ma H, Zhao W, Wang Z, Tian W, Luo L, He R (2010) The use of ultrasound for enzymatic preparation of ACE-inhibitory peptides from wheat germ protein. Food Chem 119:336–342
Jiménez-Zamora A, Pastoriza S, Rufián-Henares JA (2015) Revalorization of coffee by-products. Prebiotic, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 61:12–18
Kachrimanidou V, Kopsahelis N, Alexandri M, Strati A, Gardeli C, Papanikolaou S, Komaitis M, Kookos IK, Koutinas AA (2015) Integrated sunflower-based biorefinery for the production of antioxidants, protein isolate and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Ind Crop Prod 71:106–113
Kaderides K, Papaoikonomou L, Serafim M, Goula AM (2019) Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolics from pomegranate peels: optimization, kinetics, and comparison with ultrasounds extraction. Chem Eng Process Intensif 137:1–11
Kiani H, Sun D-W, Delgado A, Zhang Z (2012) Investigation of the effect of power ultrasound on the nucleation of water during freezing of agar gel samples in tubing vials. Ultrason Sonochem 19:576–581
Lin X, Xu J-L, Sun D-W (2019) Investigation of moisture content uniformity of microwave-vacuum dried mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus) by NIR hyperspectral imaging. LWT Food Sci Technol 109:108–117
Liu R-L, Yu P, Ge X-L, Bai X-F, Li X-Q, Fu Q (2017) Establishment of an aqueous PEG 200-based deep eutectic solvent extraction and enrichment method for pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) seed protein. Food Anal Methods 10:1669–1680
Liu Y, Sun D-W, Cheng JH, Han Z (2018) Hyperspectral imaging sensing of changes in moisture content and color of beef during microwave heating process. Food Anal Methods 1:2472–2484
Marić M, Grassino AN, Zhu Z, Barba FJ, Brnčić M, Rimac Brnčić S (2018) An overview of the traditional and innovative approaches for pectin extraction from plant food wastes and by-products: ultrasound-, microwaves-, and enzyme-assisted extraction. Trends Food Sci Technol 76:28–37
Murthy PS, Naidu MM (2012) Recovery of phenolic antioxidants and functional compounds from coffee industry by-products. Food Bioprocess Technol 5:897–903
Mussatto SI, Machado EMS, Martins S, Teixeira JA (2011) Production, composition, and application of coffee and its industrial residues. Food Bioprocess Technol 4:661
Narita Y, Inouye K (2014) Review on utilization and composition of coffee silverskin. Food Res Int 61:16–22
Pan Y, Sun D-W, Cheng JH, Han Z (2018) Non-destructive detection and screening of non-uniformity in microwave sterilization using hyperspectral imaging analysis. Food Anal Methods 11:1568–1580
Pan Y, Zhang Y, Cheng JH, Sun D-W (2020) Inactivation of listeria monocytogenes at various growth temperatures by ultrasound pretreatment and cold plasma. LWT Food Sci Technol 118:108635
Phongthai S, Lim S-T, Rawdkuen S (2016) Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of rice bran protein and its hydrolysates properties. J Cereal Sci 70:146–154
Pimentel-Moral S, Borrás-Linares I, Lozano-Sánchez J, Arráez-Román D, Martínez-Férez A, Segura-Carretero A (2018) Microwave-assisted extraction for Hibiscus sabdariffa bioactive compounds. J Pharm Biomed Anal 156:313–322
Poojary MM, Orlien V, Passamonti P, Olsen K (2017) Improved extraction methods for simultaneous recovery of umami compounds from six different mushrooms. J Food Compos Anal 63:171–183
Pu Y-Y, Sun D-W(2017) Combined hot-air and microwave-vacuum drying for improving drying uniformity of mango slices based on hyperspectral imaging visualization of moisture content distribution. Biosys Eng 156:108–119
Qin F, Johansen AZ, Mussatto SI (2018) Evaluation of different pretreatment strategies for protein extraction from brewer’s spent grains. Ind Crop Prod 125:443–453
Regazzoni L, Saligari F, Marinello C, Rossoni G, Aldini G, Carini M, Orioli M (2016) Coffee silver skin as a source of polyphenols: high resolution mass spectrometric profiling of components and antioxidant activity. J Funct Foods 20:472–485
Rommi K, Niemi P, Kemppainen K, Kruus K (2018) Impact of thermochemical pre-treatment and carbohydrate and protein hydrolyzing enzyme treatment on fractionation of protein and lignin from brewer’s spent grain. J Cereal Sci 79:168–173
Sari YW, Mulder WJ, Sanders JP, Bruins ME (2015) Towards plant protein refinery: review on protein extraction using alkali and potential enzymatic assistance. Biotechnol J 10:1138–1157
Sharayei P, Azarpazhooh E, Zomorodi S, Ramaswamy HS (2019) Ultrasound assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) peel. LWT 101:342–350
Sun H, Li C, Ni Y, Yao L, Jiang H, Ren X, Fu Y, Zhao C (2019) Ultrasonic/microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Camptotheca acuminata fruits and its antitumor activity. Carbohydr Polym 206:557–564
Talekar S, Patti AF, Singh R, Vijayraghavan R, Arora A (2018) From waste to wealth: high recovery of nutraceuticals from pomegranate seed waste using a green extraction process. Ind Crop Prod 112:790–802
Tao, Yang WD, Zhang QA, Sun D-W (2014) Ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolics from wine lees: Modeling, optimization and stability of extracts during storage. Ultrason Sonochem 21:706–715
Tiwari BK (2015) Ultrasound: a clean, green extraction technology. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 71:100–109
Vásquez-Villanueva R, Marina ML, García MC (2015) Revalorization of a peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) byproduct: extraction and characterization of ACE-inhibitory peptides from peach stones. J Funct Foods 18:137–146
Wang B, Meng T, Ma H, Zhang Y, Li Y, Jin J, Ye X (2016) Mechanism study of dual-frequency ultrasound assisted enzymolysis on rapeseed protein by immobilized Alcalase. Ultrason Sonochem 32:307–313
Wen C, Zhang J, Zhang H, Dzah CS, Zandile M, Duan Y, Ma H, Luo X (2018) Advances in ultrasound assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from cash crops – a review. Ultrason Sonochem 48:538–549
Wen L, Zhang Z, Sun D-W, Sivagnanam SP, Tiwari BK (2019) Combination of emerging technologies for the extraction of bioactive compounds. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr:1–16
Xu Y, Li Y, Bao T, Zheng X, Chen W, Wang J (2017) A recyclable protein resource derived from cauliflower by-products: potential biological activities of protein hydrolysates. Food Chem 221:114–122
Zhang P, Zhu Z, Sun D-W (2018) Using power ultrasound to accelerate food freezing processes: effects on freezing efficiency and food microstructure. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:2842–2853
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program for the financial support to the project “Waste2Fuels Sustainable production of next generation biofuels from waste streams”, grant agreement no. 654623.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the UCD-CSC Scholarship Scheme supported by the University College Dublin (UCD) and China Scholarship Council (CSC), and the Teagasc Food Research Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, L., Álvarez, C., Zhang, Z. et al. Optimisation and characterisation of protein extraction from coffee silverskin assisted by ultrasound or microwave techniques. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 11, 1575–1585 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00712-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00712-2